Environment Class 06
A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS (05:09 PM)
CONCEPT OF ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION (05:11 PM)
- It is also known as Biotic succession. It refers to a sequence of stages via which different plant community evolves till the final plant community comes and this final community does not change. This is in complete harmony.
- Barren Ground===> Now exposed to Sunlight, Winds, etc ==> Peidogenic processes (Soil forming process)==> A very thin layer of soil forms==> Low plant nutrient content, thus earliest plant life form that appears are Grasses. ==> STAGE 1
- This plant community that appears and sets it up is called the Pioneer community.
- Each stage in this succession is called Sere, and a particular community is called the Seral community
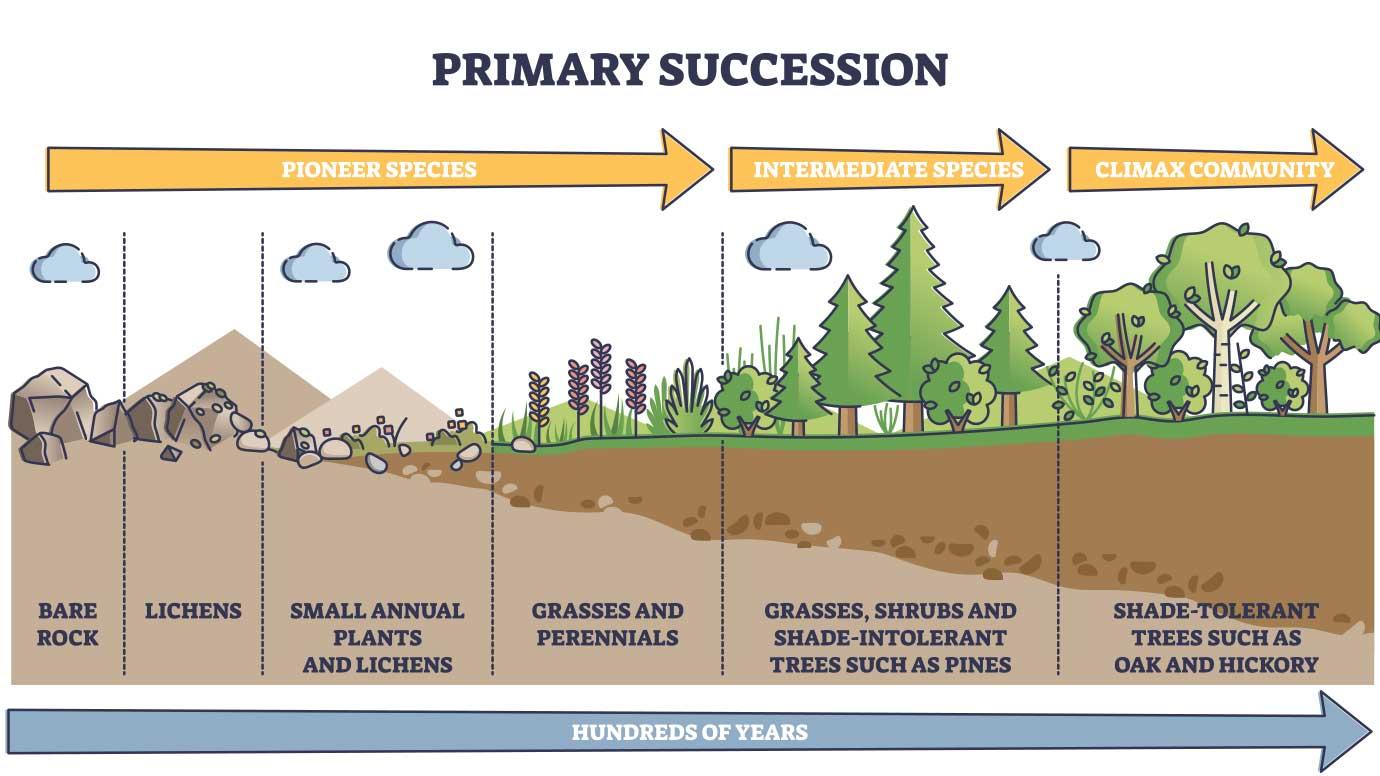
- The decay of Grasses will lead to an increase in nutrients and inorganic compounds will be added. Organic matter decays are also adding nutrients and soil is becoming thicker.
- The Pioneer community is preparing the ground for the next higher plant life forms by adding nutrients to the soil.
- Slowly grasses will be replaced with Herbs [* Herbs= Not very tall, Non-woody plants, Mainly Non-flowering, mainly used for Herbal and medicinal purposes]
- Slowly Herbs will be replaced by Shrubs [* Shrubs are woody plants, and now roots will be well developed as the soil is thick enough to support the medium-height trees]

- In the meantime, Animal organisms are also increasing. Once the grasses colonize the ground then the animal organisms start multiplying in terms of species and population.
- A favourable climate is now developed because of the thick soil and food availability.
- Shrubs will be replaced by Trees. These will not be replaced by any other community. These communities are in complete harmony with the climate. These trees are in complete balance with the climatic factors. These are called Climax Communities.
- Assumption- Climatic conditions are such that they are providing sufficient conditions for the development of trees such as temperature and precipitation.
- Ecological successions when gets completed then the Ecosystems are created.
- The collection of ecosystems is called Biomes.
- Note- All the ecosystems which are found today must have formed in the last 40-50 million years (Mostly in the Cenozoic era). The ecosystems can also be found which are formed in the Mesozoic era but they are very rare.
- Ecological succession can start from Barren ground- Primary succession
- When ecological succession starts on the Lava which is now spread over the biome then also it is called Primary succession as the lava which is now solidified is barren land.
- Ecological succession can start in a region where there was vegetation but the vegetation is now destroyed by an earthquake or natural catastrophe and if the ecological succession starts- Secondary succession
- Example- Most forests of North America and Europe are examples of Secondary Succession as the forest developed were completely destroyed by Human activity and again the ecological succession started.
- Lifeforms prepare the ground for the higher plant to grow. When this plant life helps in ecological succession then it is called Autotrophic succession/ Autogenic succession.
- When the animal species or non-plant life help in ecological succession - then it is called Heterotrophic succession/ Allogenic succession.
- When ecological succession starts in the water- Hydrosere
- When ecological succession starts at land- The lithosphere
- Notes
- Ecological succession is a period of time within which plant communities replace each other till the establishment of a final plant community which is called the Climax plant community.
- The ecological succession in a region that never had any plant life and there for which starts on the barren ground starts with the first plant community in the form of Grass which is the Pioneer plant community.
- The Pioneer plant community is the first plant community to come into being and it is always made up of grass. Slowly this plant community is replaced by the Herbs which are low-height plants without Woody stems and which have a short life cycle.
- This plant community could come into being because geographic processes have continued to develop soils with the soil becoming more thicker and the nutrient contents in the soil becoming more. The soil nutrient content is increasing not only because of the breakdown of rocks releasing minerals and nutrients but also because of the decomposition of dead organic matter.
- These processes always continue as the ecological succession goes forward. The herb community is slowly replaced by shrubs which are medium-height Woody trees that can now develop in the region because the soils are thick enough to get mechanical support and where the soil has enough nutrients to support such plants.
- The Shrubs are finally replaced by tall trees which are in complete equilibrium/ balance with climatic conditions and the soil conditions. Therefore these tall trees will not be replaced by any other plant community. This is called the Climax plant community.
- Ecological succession comes to an end with the establishment of a climax plant community.
- As the ecological succession goes forward the no. of animals and species of animals also multiply because of more and more favourable conditions, therefore when the ecological succession has completed a community of plant and animal life forms would have been established creating a series of Ecosystems in the region with a food chain.
- [* Climax plant community will be ultimately decided by Climate. If the climate is sub-humid then climax community then Grass + herbs, If the climate is cool then grass. In the desert, the succession will stop at the herbs stage only. ]
- Biomes- Collection of natural ecosystems in the given climatic belt. Example- Equatorial forest biome. Ecological succession leads to the creation of the Biome.
BIOMES (06:23 PM)
- Any Biome is a collection of close and natural ecosystems. Each biome has one climax community.
- Biomes are divisions of the earth's land surfaces and this division is based on vegetation types. Example- Equatorial forest, Savannah Biome
- Biomes classification
- a) Forest Biomes
- b) Grassland biomes
- c) Desert Biomes - Hot desert, Cold desert, Tundra region, etc
- Biomes of the Earth's surface- Terrestrial Biomes
- Equatorial Forest biomes (0-10 degrees in each hemisphere)
- Three-layered vegetation- Lowermost strata of vegetation, this is made of shrubs. Medium-height trees constitute the middle layer of vegetation. Tall trees whose height is rising of medium height trees.
- Canopy- Branches and leaves covering the ground.

- The upper 1/3rd is called as Emergent layer- Leaves are broad, hardwood. Emergent trees have maximum life forms.
- Maximum Animal life in the equatorial forest biome is part of the tall trees on the top with a lot of birds and bats.
- The next most abundant region for animal life is the ground-level vegetation with a lot of ground-level birds and mammals and Million of insects living in the soil and on the ground.
- Index plants- They indicate the type of plant.
- Index plants of the equatorial biome- Rosewood, Natural Rubber, Mahogany, Ebony.
- Distinct characters- Liana Forest and Epiphytes.
- Region- Amazon River basin.
- Note- This biome has the maximum species diversity both in animal and plant life. Examples- Amazon River Basin, Congo River Basin, South East Asia Equatorial region, West Central Africa- Lenin, Ghana, Togo, etc.
- Tropical rainforest biome (20-30 degrees N/S)
- This biome has all the characteristics of the equatorial biome.
- Difference from Equatorial biome- Epiphytes are less, Lianas are less, Lesser species diversity, Higher latitude.
- Index plants- Mahogany, Ebony, Natural Rubber, etc
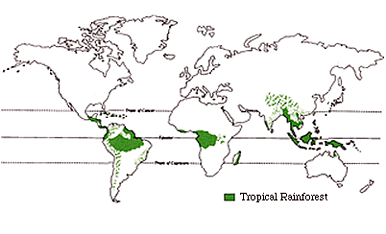
- Region- Eastern edge of Brazil, Eastern Edge of Madagascar, All islands of West Indies, Windward region of Western Ghat, Andaman & Nicobar, West coast of Myanmar (Arakan coast), South East Asia outside the Equatorial Belt (Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam), Eastern Edge of Australia.
- Temperate Evergreen Forest biome
- Climate- China type of climate (Warm to hot summers and cool winters) (25-40 degree latitude), Rainfall is heavy in summer
- It is like a rainforest in the middle Latitudes
- Biome characteristics- Lower lever vegetation is too layered i.e. Ground-level vegetation is well developed, Tall trees may be softwood and hardwood
- Hardwoods are Hickory, chestnut, etc whereas Softwoods are represented by Oak, Pine, Spruce, Fir, etc.
- Ephiphytes and Lianas are there but they are in the form of Mosses and Lichens growing from tree trunks.
-
Mosses Lichens Low-level plants that can do photosynthesis The symbiotic relationship between Algae and Fungi Soft, non-woody stem, Leaves are present Algae provide food and Fungi provide protection They are not vascular i.e. no xylem and phloem Fungi can not carry photosynthesis Height is dwarf. [3-4 inches from ground] They are also non-vascular They are Cryptograms i.e. they can not reproduce with seeds. They reproduce with spores. Height is also small They belong to Bryophytes They can grow on bare rocks - Region- Southeastern China, Southeastern Australia i.e. Sydney, Southeastern Brazil (Rio de Janeiro, Sao Paulo), Southeastern USA i.e. Florida, etc

TEMPERATE DECIDUOUS FOREST BIOME (07:27 PM)
- When the trees drop their all the leaves in dry season= Deciduous
- Climate- The Laurentian type climate/ Manchurian type of climate (35-55 degrees N/S), It also includes the British type of climate.
- Characteristics- Very cold winter, Summers are warm, Rain is in the summer season
- Index plants- Softwoods- Spruce, Birch, Oak, Fir, and climax Hardwoods- Maple, Beech, Juglang (Walnut)
- Biome Characteristics- The lower layer is very weakly developed.
- Region- Northeastern China, Northeastern USA, Laurentia region of Canada, New Zealand, Western Europe, Rain-shadow regions of the Western part of North America (Leeward side of the mountains), etc
TROPICAL DECIDUOUS FOREST BIOME (07:37 PM)
- It is also called a Monsoon forest biome.
- Climate- Monsoon climate i.e. Hot summer, Heavy Rain in summer, cool to warm winter.
- Characteristics- Open growth of trees i.e. Trees and then open ground, Trees are having very thick trunks, the Width of the trunk is massive, the Barks are very thick, and these are Hardwoods.
- Leaves are broad but they are habituated in deciduous settings i.e. they lose the leaves in the dry season. These are characterized by Huge areas covered with Bamboo.
- Species diversity- Lot of species diversity.
- Index plants- Sal and Teak.
- Biome characteristics- The lower layer of vegetation is very well developed.

- Region- Asia region, Peninsular South East Asia, South Asia- India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, North Australia, Southern China.
MEDITERRANEAN FOREST BIOME (07:44 PM)
- It is part of the Mediterranean climate.
- Characteristics- No rain in summer, Westerlies come onshore on the edges of the landmass, Summers are dry (Influence of Sub-tropical high-pressure belt).
- Biome characteristics- Vegetation is evergreen despite the dry season.
- [* Why the vegetation is evergreen?- Forest biome is developed at the edges of the continent which is exposed to the ocean. As they are exposed to the ocean thus moisture availability is there. In the dry season, the forest biome is getting its water supply from underground water.]
- [* Adaptation by trees to withstand dryness- Leaves are waxy to prevent transpiration loss, Roots go deep, and Trees are shrubs to minimize the surface area]
- Index plant- Olive, Oak, Cork, etc
- In this biome, a lot of deforestation happened so there are Secondary succession created forests.

TAIGA FOREST BIOME (07:52 PM)
- Climate- A Siberian type of climate
- Climate characteristics- Winter temperature goes around -65 degrees, Very short summer of 3 months, Very short cool summer, Rainfall is very little, and that too in summer, evaporation and Transpiration is very less and thus evergreen forests are found.
- Adaptation by trees- Leaves are needle-shaped and trees are coniferous.
- 1000s of hectares of one species is found which is called "Pure Strand". These are softwood.
- Index species- Spruce, Pine, Fir, and Larch.
- Region- Siberia, Northern Canada, Northern Part of Europe (Norway, Finland), Alaska.
- Boreal Forest- Taiga forest in the Northern part of the USA and Russia (Siberia) and western Europe is called the Boreal forest.
- Eastern Siberia's boreal forest is Larch dominated Whereas Western Siberia, Central Siberia, and the Rest of other Boreal forest is Spruce, pine, and Fir dominated.

- Ground-level vegetation is very weak. Leaves are very waxy and they can't decompose easily as the soil bacteria are very few.
- [* If the leaves are broken down then it would have released non-organic compounds and it would have supported the ground-level vegetation. But here the decomposition is not happening]
TUNDRA FOREST BIOME (08:01 PM)
- Arctic Tundra- Polar regions
- Alpine Tundra- The same type of climate in the high altitude of Tall Mountains. For Example- Mount Kilimanjaro at the equator has a tundra type of climate at the higher slopes.
- Vegetation- Mosses and Lichens only. These do not have true plants.
- Primary producers= Mosses and Algae part of Lichen.
- Herbivores- Lemmings, Musk oxen, Caribou, Reindeer.
- Higher Animals- Arctic foxes, wolves, Humans, and Polar bears.
- In Alpine Tundra, At 2900-3500 meters coniferous forests are found in the Himalayas, At 4500-meter heights the Alpine tundra are found (Mosses and Lichens).

GRASSLAND BIOMES (08:09 PM)
- Tropical Grassland- These are part of the Savanah setting (10-20 degrees N/S).
- Savanah Forest Biome (10-20 Degrees )
- Climate characteristics- Rainfall in Summer, Warm Winters, Hot summers, Alternate Wet and Dry season.
- Biome characteristics- A lot of grass is present along with Shrubs as trees. The grass is dominant and the trees are less.
- Trees- Acacia species, Wild date.
- Grass- Grass is very tall (Elephant Grass), Coarse grass is not eatable by livestock.
- Region- Australia, Africa, South America (Llanos in Venezuela & Colombia and Campos in Brazil and Argentina)
- Tropical Grassland Biome
- Grassland biome- Coarse, Thorny, and Shrubs are trees
- This is also called Parkland, Bushveld as trees are few and scattered and Grass is more.

- Climax/ Index species- Acacia.
- African Savannah- It has special trees called Baobabs. It stores water in its Trunk.

- Temperate Grassland Biome (Sub-tropical to Middle latitude) (25-30 N/S)
- Characteristics- Cool winters, Warm Summer with Sub humid to semi-arid rain-like conditions
- No trees at all, Grass is soft and edible by livestock, Grass is evergreen, Grass is dominant
- Examples- Steppes grassland (Kazakhstan and Russia), Prairies of North America, Pampas in Argentina and Uruguay, Velds in South Africa, and Downs in Australia (Basin of Murray and Darling).
- Climax vegetation- Grass
- Index grass- Herb (Non -woody, soft stem, some are flowering), Forb (Broader leaves, Non-woody, Flowering, Soft stems), Grass (Non-woody, Leaves grow directly from the stem and not from the branches of the stem, they curl around the stem).
- Grass is of two species i.e. Alpha-Alpha, and Lucerne.
The topic for the next class- Marine Biome, Desert Biomes, Forest ecosystems, Deforestation, India's forest, and Bio-diversity.